A Strong Contract ADC Market Drives Expansions in High-Potency Manufacturing
Driven by strong demand in the oncology drug market, high-potency manufacturing continues to be an active area of investment for CDMOs/CMOs for both drug substances and drug products. Growth in the contract market for antibody drug conjugates, one component, is projected in the double-digits.
By Patricia Van Arnum, Editorial Director, DCAT, pvanarnum@dcat.org
Contract ADC market growth
High-potency manufacturing continues to be an active area of investment for CDMOs/CMOs, largely driven by strong growth in the market for antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) as both large and smaller bio/pharmaceutical candidates advance their pipelines in this area with oncology being the leading therapeutic area driving this growth.
ADCs are composed of both biologic and small-molecule components and consist of a small-molecule compound (for oncology applications, typically a cytotoxic compound) linked to a monoclonal antibody. For CDMOs/CMOs specializing in high-potency manufacturing, the manufacture of an ADC requires specialized conditions under high-containment to produce the cytotoxic small-molecule compound and conjugation capabilities to link the small-molecule compound to the monoclonal antibody. Similar high-containment conditions are required for the manufacture of the drug product.
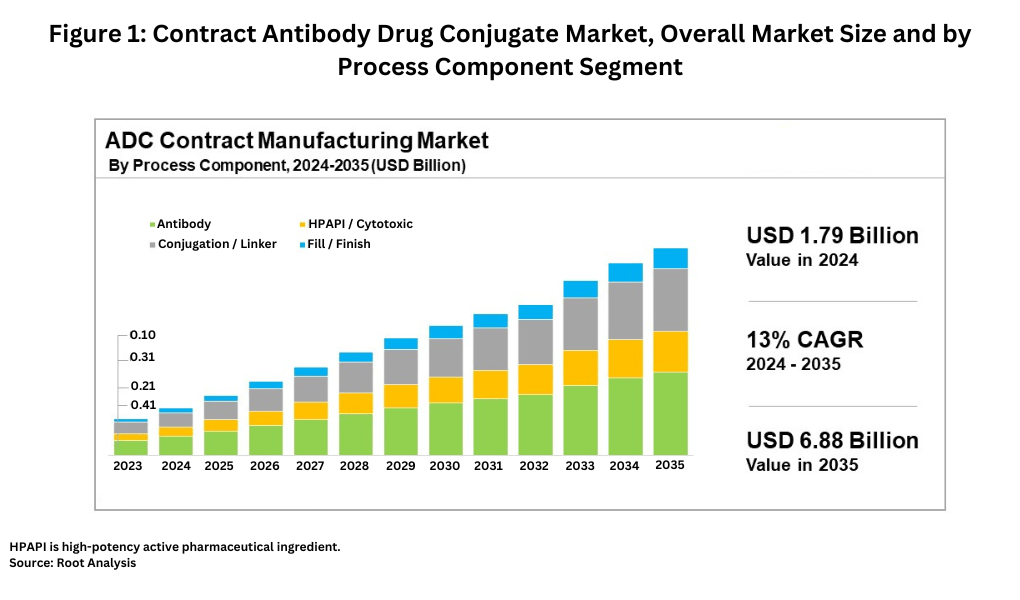
The global ADC contract manufacturing market is estimated at $1.79 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13% to reach approximately $6.87 billion by 2035, according to a recent market study by Root Analysis, a business research and consulting firm serving the bio/pharmaceutical industry. Based on process component, the contract ADC market is divided into four major segments: the antibody, the highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredient (HPAPI)/cytotoxic payload, the conjugation/linker, and the fill–finish of the final drug product. The antibody component of the market represents the largest share, accounting for approximately 40% of the contract ADC market, followed by the conjugation/linker segment at 30%, the HPAPI/cytotoxic payload segment at 20%, and the fill–finish segment at 10%. Figure 1 outlines the market size, growth rates, and segments for the contract ADC market.
Roundup of recent investments
With this growth, CDMOs/CMOs are increasing development and manufacturing capacity to support ADCs. A roundup of recent investments (announced thus far in 2024 and in late 2023) are outlined below.
Lonza. Lonza is increasing bioconjugation capacity by adding two new bioconjugation suites at its site in Visp, Switzerland. This expansion is expected to be one of the largest bioconjugation facilities globally (1,500 m²) when operational in 2026.
Last year (2023), Lonza acquired Synaffix B.V., a company with a technology platform for ADCs, bispecific antibodies, and other targeted therapeutics. The companies are advancing their Center of Excellence for Bioconjugate Technology Development.
On the drug product side, Lonza is adding a dedicated commercial-scale aseptic cGMP filling line at its site in Stein, Switerland, to be operational by 2027. This new filling line will handle and fill bioconjugates for the commercial supply of ADCs.
MilliporeSigma. MilliporeSigma announced last month (October 2024) a $76-million expansion of its ADC manufacturing capabilities and capacity at its Bioconjugation Center of Excellence in St. Louis, Missouri. The investment will triple existing capacity and upgrade 34,000 square feet to support process and analytical development, quality control, research and development, manufacturing, and logistics. The expansion will add new labs, a dedicated manufacturing buffer preparation facility, and a cold-storage and a GMP-controlled room temperature warehouse that will be located close to its existing facility. The expansion will support early-stage and commercial bioconjugates.
The expansion is the latest by the company in ADC-based services. In 2022, the company opened a $65-million, 70,000-square foot facility in Verona, Wisconsin, to double the production of HPAPIs used in cancer therapies, including ADCs. In September 2024, the company launched the Mobius ADC Reactor, a scalable single-use mixer specifically designed for ADC manufacturing. The company also launched ChetoSensar, a technology that alleviates ADC solubility challenges as well as the ADCore portfolio of advanced payload intermediates.
Veranova. In June (June 2024), Veranova (formerly known as Johnson Matthey Health, the fine chemicals business of Johnson Matthey) initiated a $30-million expansion of its ADC and highly potent compound development and manufacturing capabilities at its Devens, Massachusetts, facility. The expansion will include a new high potent process development laboratory and two new cGMP suites designed to handle potent compounds with occupational exposure limits of less than 0.01 µg/m³. These facilities, equipped to manage high-potency compounds, ADC linker-payloads, and other complex molecules, will feature dedicated air-handling systems, airlocks for clean-in-place operations, isolator technology, and a range of processing capabilities, including synthesis reactors, chromatography, thin-film evaporators, and lyophilization.
Olon. Earlier this month (November 2024), Olon announced the schedule for the construction of a new EUR-25-million ($27-million) facility in Rodano (Milan), Italy, dedicated to ultra-potent compounds. The company has completed the installation and validation of a new-small scale production area within the facility. The installation of the plant for large-scale production will be completed shortly, with completion scheduled for January 2025. The commercial-scale line will be fully integrated with the small-scale line. The new plant, designed to produce payloads, linker payloads, and ultra-potent APIs, is now ready to accommodate small-scale GMP production. Separately, Olon is adding a GMP high-potency API suite at the company’s site in Concord, Ohio, the company’s Center of Excellence for early development of APIs.
Piramal Pharma Solutions. In December (December 2023), Piramal Pharma Solutions opened an £45-million ($57-million).expansion of its ADC manufacturing facility in Grangemouth, Scotland, UK. The expansion increases the site’s capacity by approximately 70% to 80% to enable scale-up of commercial ADC manufacturing batches. The capacity expansion features two new ADC manufacturing suites to complement the existing three and has been designed to accommodate further expansion. Potential future enhancements may include a new sterile fill–finish suite dedicated to ADCs and two additional large-scale manufacturing suites capable of handling increased batch sizes.
Sterling Pharma. Sterling Pharma Solutions announced last month (October 2024) the second phase of an expansion plan at its Deeside, UK, site to support ADC development, with a more than £10 million ($13 million) investment to increase GMP bioconjugation capacity. A new 2,300-square foot suite is being commissioned for clinical-scale manufacturing using reactors up to 500 liters in volume, which will more than double the site’s existing capacity.
The new suite will include a 1,400-square-foot Grade C cleanroom for ADC manufacturing, and will use both flexible and hard-containment technologies to handle highly potent molecules with exposure limits down to 0.01 micrograms per cubic meter (occupational exposure Band 5). Existing ancillary GMP facilities at the site for buffer and reagent preparation, waste disposal, water-for-injection generation as well as analysis and quality control laboratories will support the new manufacturing suite. The site will also upgrade its stability chamber capacity for the storage and monitoring of final products. Completion of the project is expected in early 2026.
In June (June 2024), Sterling Pharma announced a $3-million investment at its Germantown, Wisconsin, facility, to expand its ADC development and manufacturing capabilities. The company commissioned a dedicated GMP suite at the site, which will incorporate the installation of a modular isolator with containment capabilities down to less than 1 nanogram per cubic meter.
Siegfried. In July (July 2024), Siegfried acquired an early-phase drug-substance manufacturing site in Grafton, Wisconsin, from Curia. Siegfried plans to develop the site into a hub for early-phase CDMO services, including services for projects for HPAPIs, the company said at the time of the announced acquisition in June (June 2024).







