Blockbuster Muscle: Small Molecules or Biologics?
Which modality, small molecules or biologics, leads among the top-selling products? A look at the top-selling products industry-wide and blockbusters from select leading bio/pharma companies provides the answer.
Modality of top-selling products
In looking at the top 20 products, based on 2020 sales based on an analysis from EvaluatePharma (1), biologics have a slight edge over small molecules among the top 20 products, with biologics accounting for 12 products, or 60%, and small molecules accounting for 8 products, or 40%.
The top-selling small-molecule drugs from 2020 were: Bristol-Myers Squibb’s Revlimid (lenalidomide); Pfizer’s and Bristol-Myers Squibb’s Eliquis (apixaban); AbbVie’s and Johnson & Johnson’s Imbruvica (ibrutinib); Gilead Sciences’ Biktarvy (bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide); Bayer’s and Johnson & Johnson’s Xarelto (rivaroxaban); Pfizer’s Ibrance (palbociclib); Pfizer’s and Astellas Pharma’s Xtandi (enzalutamide); and AstraZeneca’s Tagrisso (osimertinib).
The top-selling biologics, including drugs and vaccines, in 2020 were: AbbVie’s Humira (adalimumab); Merck & Co.’s Keytruda (pembrolizumab); Bayer’s and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals’ Eylea (aflibercept); Johnson & Johnson’s Stelara (ustekinumab); Merck & Co.’s Opdivo (nivolumab); Amgen’s Enbrel (etanercept); Pfizer’s Prevnar 13 (Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine); Roche’s Avastin (bevacizumab); Eli Lilly and Company’s Trulicity (dulaglutide); Roche’s Ocrevus (ocrelizumab); Roche’s and Biogen’s Rituxan (rituximab); and Johnson & Johnson’s Remicade (infliximab).
New drug approvals: small molecules versus biologics
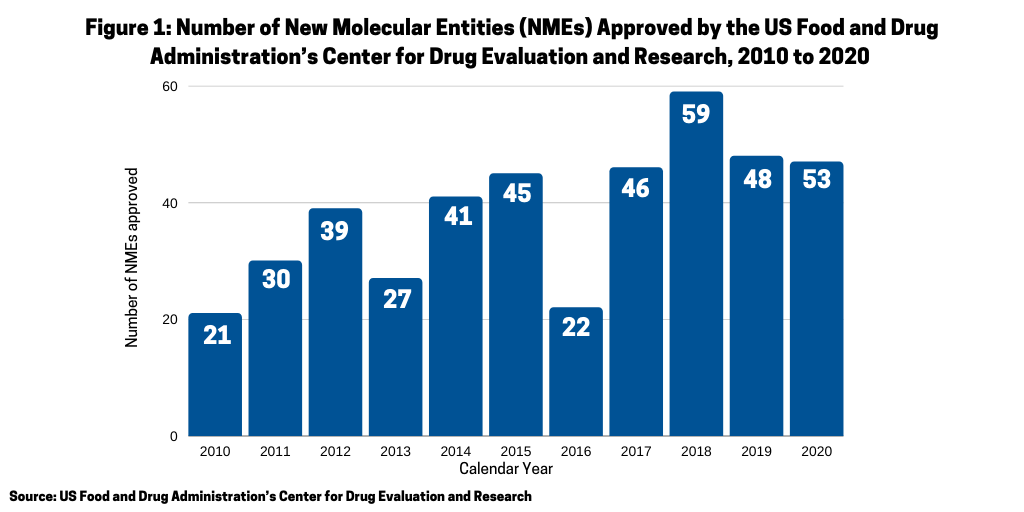
Another measure of the relative strength of each modality, small molecules or biologics, is to look at recent new drug approvals. In 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) approved 53 new molecular entities (NMEs), which surpassed the 48 NMEs approved in 2019 and was the second highest level of NMEs approved in the past decade, except for 2018 when 59 NMEs were approved (see Figure 1).
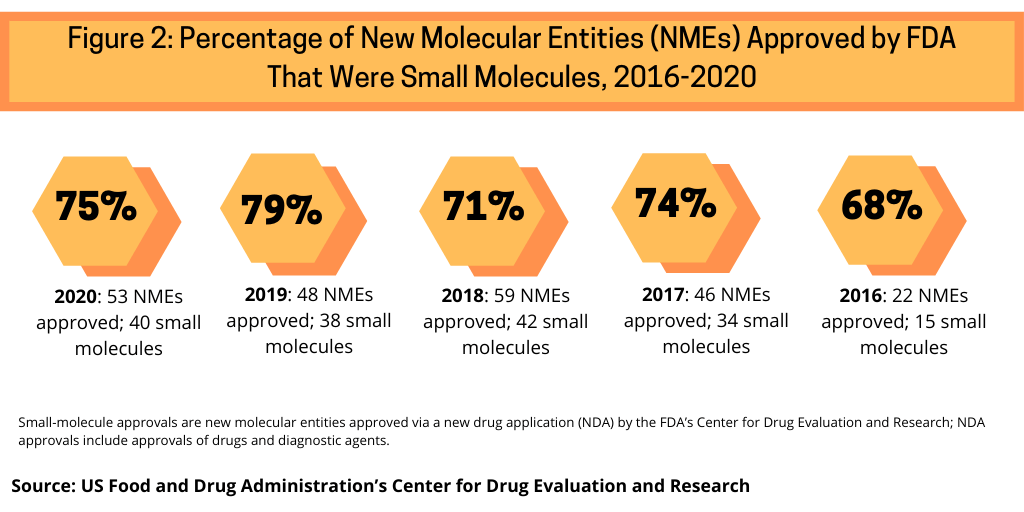
Continuing a trend, small-molecule drugs dominated NME approvals in 2020. In 2020, 75% or 40 of the 53 NMEs approved in 2020 were small molecules (see Figure 2). This continues a recent trend of having approximately three-fourths of NME approvals be small molecules. In 2019, 79% of NME approvals were small molecules; in 2018, it was 71% and 74% in 2017.
Potential blockbusters: small molecules and biologics
New drug approvals from the FDA are expected to generate significant value in 2021 with 10 drugs projected to launch in 2021 with potential blockbuster status by 2026, according a recent report by Evaluate Vantage using EvaluatePharma data. Blockbusters are defined as products with sales of $1 billion or more.
Table I at the end of the article outlines the top 10 blockbuster contenders to be launched in 2021 and projected to achieve blockbuster status by 2026. Of these 10 potential blockbusters, five are biologics and five are small molecules. The five projected small-molecule blockbusters are: Bristol-Myers Squibb’s mavacamten; Axsome Therapeutics’ AXS-05; ChemoCentryx’s/Vifor Pharma’s avacopan; Aurinia Pharmaceuticals’ voclosporin; and Pfizer’s abrocitinib. The five biologics are Biogen’s and Eisai’s aducanumab; Argenx’s efgartigimod, an antibody fragment; UCB’s bimekizumab; Ascendis Pharma’s TransCon hGH (long-acting human growth hormone); and Bristol Myers Squibb’s/bluebird bio’s idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel). Four of the five projected top-selling blockbusters for 2026 (based on launch in 2021) are biologics (see Table I at the end of the article). Highlights of some of the leading contenders are outlined below.
Biogen’s and Eisai’s aducanumab. Biogen’s and Eisai’s aducanumab, a biologic drug to treat Alzheimer’s disease, is the biggest potential launch in 2021 with $4.8 billion in forecast sales in 2026; however, the approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the drug earlier this year (2021) has raised some concerns. In November (November 2020), an advisory committee of the FDA voted to reject approval of aducanumab, citing that the drug failed to demonstrate efficacy and more research was needed. FDA advisory committee recommendations are non-binding although they have historically been taken by the full FDA when considering a drug for approval. The companies announced in late January (January 2021) that the FDA extended the review period for the biologics license application (BLA) for aducanumab by three months from March 7, 2021 to June 7, 2021. As part of the ongoing review, Biogen submitted a response to an information request by the FDA, including additional analyses and clinical data, which the FDA considered a major amendment to the application that required additional time for review. Biogen submitted the aducanumab BLA to the FDA in July 2020. The FDA accepted the BLA in August 2020 and granted priority review. It approved the drug in June (June 2021).
Aducanumab is an amyloid beta-targeting antibody that has shown in clinical trials to remove amyloid beta in the brain and slow clinical decline in patients with mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease and mild Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Biogen licensed aducanumab from Neurimmune, Zurich, Switzerland-based bio/pharmaceutical company. Since 2017, Biogen and Eisai have collaborated on the development and commercialization of aducanumab globally.
Argenx’s efgartigimod. Another biologic slated for blockbuster status by 2026 is efgartigimod, a biologic being developed by Argenx, a Breda, the Netherlands-based bio/pharmaceutical company, for treating generalized myasthenia gravis, a rare muscular disease. The Evaluate Vantage report projects 2026 estimated sales of $2.5 billion. In March (March 2021), the FDA accepted the company’s BLA for the drug. The FDA has set a standard 10-month review process with a target action date of December 17, 2021.
Bristol-Myers Squibb’s mavacamten. Bristol-Myers Squibb’s (BMS’) mavacamten is a small-molecule drug for treating cardiomyopathy, which is expected to launch in 2021 with potential blockbuster status with 2026 estimated sales of $2.0 billion according to the Evaluate Vantage report. BMS gained mavacamten through its $13.1-billion acquisition of MyoKardia, a Brisbane, California-based bio/pharmaceutical company focused on cardiovascular diseases. In March (March 2021), the FDA accepted the company’s new drug application for mavacamten for treating symptomatic obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM). The FDA has assigned a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) goal date of January 28, 2022, so potentially moving product launch to 2022. BMS says it expects to progress mavacamten in additional indications, including non-obstructive HCM.
UCB’s bimekizumab. Another biologic with blockbuster potential slated to be launched in 2021 is UCB’s bimekizumab, a biologic for treating psoriasis. The Evaluate Vantage report projects 2026 estimated revenues of $1.6 billion. Bimekizumab is an investigational IL-17A and IL-17F inhibitor that is currently under review by the FDA and the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in adults. The FDA has set a PDUFA review date of October 15, 2021. The European Commission approved the drug last month (August 2021).
Bristol Myers Squibb’s/bluebird bio’s idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel). BMS and bluebird bio, a Cambridge, Massachusetts bio/pharmaceutical company, are advancing idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-directed genetically modified autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell immunotherapy, for treating multiple myeloma. The Evaluate Vantage report projects 2026 estimated revenues of $1.5 billion. In March (March 2021), the FDA approved the therapy for treating adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma after four or more prior lines of therapy, including an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody. Last month (August 2021), the European Commission approved Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel) for treating relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma.
Ascendis Pharma’s TransCon hGH (lonapegsomatropin). Ascendis Pharma, headquartered in Hellerup, Denmark, is advancing TransCon hGH (lonapegsomatropin), an investigational long-acting prodrug of somatropin (human growth hormone or hGH) that releases somatropin with the identical amino acid sequence and size as daily growth hormone. It is designed as a once-weekly treatment for growth hormone deficiency. The Evaluate Vantage report projects 2026 estimated revenues of $1.5 billion. Last month (August 2021), the FDA approved Skytrofa (lonapegsomatropin-tcgd) for the treatment of pediatric patients one year and older who weigh at least 11.5 kg and have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone.
The full listing of 10 projected blockbusters, based on 2026 estimated revenues, may be found in Table I below.
Table I: Projected Biggest Product Launches in 2021 with Potential Blockbuster Status Based on 2026 Estimated Worldwide Sales
| Product; molecule type | Product Type/Indication | Company | 2026 Estimated Worldwide Sales |
| Aducanumab; biologic | Anti-beta amyloid mAb for Alzheimer’s disease | Biogen/Eisai | $4.8 Bn |
| Efgartigimod; biologic | Anti-FcRn mAb for IgG-mediated autoimmune diseases | Argenx | $2.5 Bn |
| Mavacamten; small molecule | Cardiac myosin inhibitor for cardiomyopathy | Bristol-Myers Squibb | $2.0 Bn* |
| Bimekizumab; biologic | Anti IL-17A&F mAb for psoriasis | UCB | $1.6 Bn |
| TransCon hGH (lonapegsomatropin); biologic | Long-acting human growth hormone | Ascendis Pharma | $1.5 Bn |
| Idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel); biologic | Anti-BCMA Car-T therapy for myeloma | Bristol Myers Squibb/bluebird bio | $1.5 Bn |
| AXS-05; small molecule* | NMDA receptor antagonist for treating depression | Axsome Therapeutics | $1.2 Bn |
| Avacopan; small molecule | Complement factor C5a inhibitor for vasculitis | ChemoCentryx/Vifor Pharma | $1.2 Bn |
| Voclosporin; small molecule | Calcineurin inhibitor for lupus nephritis | Aurinia Pharmaceuticals | $1.1 Bn |
| Abrocitinib; small molecule | JAK-1 inhibitor for atopic dermatitis | Pfizer | $1.0 Bn |
Bn is billion; mAb is monoclonal antibody.
* Forecasts from analysts covering MyoKardia, ahead of BMS buyout. Decision on BMS’ liso-cel (2026 estimated sales of $1.2 billon) could also come in 2021, delayed from 2020.
Listing excludes COVID-19 products.
Note: In August 2021, the FDA announced that hat its review of the new drug application for AXS-05 for the treatment of major depressive disorder would not be completed by the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of August 22, 2021. The FDA did not request additional information from the company, and the review of the application is ongoing.
Source: EvaluatePharma, Evaluate Ltd. and company information
Reference:
1. E. Sagonowsky, “Special Reports: The Top 20 Drugs by Worldwide Sales in 2020,” FiercePharma, May 3, 2021.